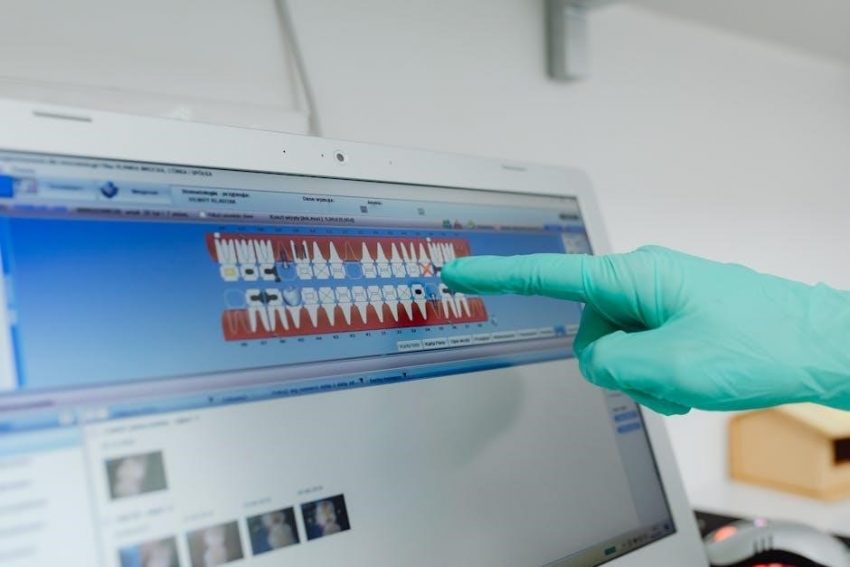
The surgical guide dental code refers to a customized tool aiding precise implant placement, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in dental procedures. It is developed from patient-specific data, combining digital imaging and anatomical information to guide surgeons during operations. This innovative approach minimizes errors, enhances predictability, and improves patient outcomes. By adhering to ADA and CDT coding standards, it ensures proper documentation and billing processes.
Definition and Purpose
A surgical guide in dentistry is a customized plastic tool designed to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of dental implant placement. It serves as a precise template, guiding the surgeon during procedures to ensure optimal positioning and alignment of implants. The purpose of a surgical guide is to translate pre-surgical planning into real-time clinical application, minimizing errors and improving patient outcomes. Developed from patient-specific data, including CBCT scans and 3D imaging, these guides are tailored to individual anatomical needs. They play a critical role in reducing complications, enhancing healing, and ensuring predictable results, making them an essential component in modern dental surgery.
Importance in Dental Surgery
Surgical guides play a pivotal role in dental surgery by enhancing precision, reducing complications, and improving outcomes. They ensure accurate implant placement, minimizing errors and promoting optimal healing. These guides streamline the surgical process, saving time and reducing patient discomfort. By providing a clear roadmap for surgeons, they enhance confidence and consistency in procedures. Surgical guides also contribute to better patient satisfaction by ensuring aesthetically pleasing and functional results. Their use is particularly critical in complex cases, where anatomical challenges require exact positioning. Overall, surgical guides are indispensable tools in modern dental surgery, combining technological advancements with clinical expertise to deliver superior care.

Types of Surgical Guides
Surgical guides are categorized into custom and generic, with digital and traditional options. Custom guides are patient-specific, using CBCT scans for precise fit. Generic guides are pre-fabricated, cost-effective solutions. Digital guides utilize 3D imaging, while traditional guides rely on physical models, offering varying accuracy and applications in dental procedures.
Custom vs. Generic Guides
Custom surgical guides are tailored to individual patient anatomy using CBCT scans and 3D imaging, ensuring precise implant placement. They are ideal for complex cases, offering enhanced accuracy and fit. Generic guides, however, are pre-fabricated and less expensive, suitable for routine procedures. Custom guides reduce surgical time and minimize errors, while generic guides are more cost-effective but lack the same level of precision. The choice between them depends on the complexity of the procedure, patient-specific needs, and budget considerations. Custom guides are preferred for accuracy, while generic guides provide a practical solution for straightforward cases.
Digital vs. Traditional Guides
Digital surgical guides utilize advanced technology like CBCT scans and CAD/CAM software for precise customization, offering superior accuracy and integration with modern implant systems. They enable detailed pre-surgical planning, reducing errors and operational time. Traditional guides, while effective, rely on physical impressions and manual fabrication, making them less precise for complex cases. Digital guides enhance predictability and patient outcomes, particularly in challenging anatomical scenarios. They also allow for real-time adjustments and better visualization. Traditional guides, however, remain cost-effective and suitable for straightforward procedures. The shift toward digital solutions reflects the dental industry’s embrace of technological advancements for improved surgical outcomes and streamlined workflows.
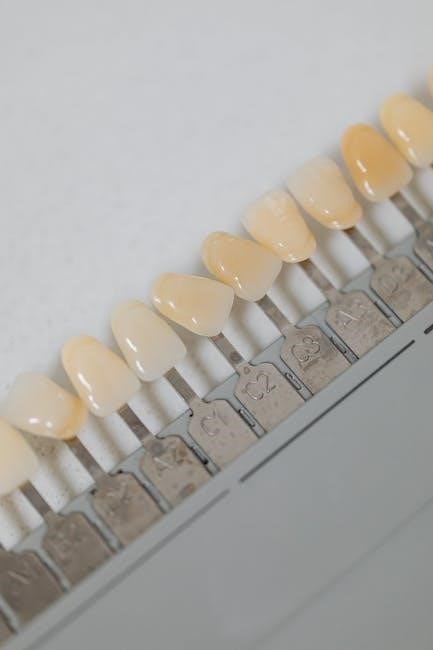
Key Components of a Surgical Guide
A surgical guide’s key components include anatomical fit, durable materials, precise design, and fabrication process, ensuring accuracy and patient-specific outcomes in dental surgeries.
Anatomical Fit and Accuracy
Anatomical fit and accuracy are critical components of a surgical guide, ensuring precise alignment with the patient’s jaw and surrounding structures. Advanced technologies like CBCT scans and 3D imaging enable highly detailed models, allowing for customized guides that match individual anatomy. The guide’s design must account for bone density, nerve locations, and adjacent teeth to avoid complications. High accuracy minimizes surgical errors, reducing the risk of implant misplacement. CAD/CAM software further enhances precision, enabling surgeons to plan and execute procedures with confidence. Proper anatomical fit ensures optimal implant placement, improving both functional and aesthetic outcomes for patients. This level of accuracy is essential for successful dental surgeries, making it a cornerstone of modern implantology practices.
Material and Durability
The choice of material for surgical guides is crucial for their durability and performance. Commonly used materials include 3D printed resin, metal, and sterilizable plastics, each offering unique benefits. These materials must withstand sterilization processes without losing shape or integrity, ensuring patient safety. The guide’s durability is essential for maintaining accuracy during surgery, as any deformation could lead to placement errors. High-quality materials also extend the lifespan of reusable guides, making them a cost-effective option for dental practices. Advances in material science have introduced biocompatible and lightweight options, enhancing both functionality and patient comfort. The combination of durable materials and precise fabrication ensures that surgical guides remain reliable tools in modern implantology.
Design and Fabrication Process
The design and fabrication of surgical guides involve advanced technologies to ensure precision and customization. The process begins with capturing patient-specific data through CBCT scans and 3D imaging, which are then used to create a digital model. CAD/CAM software is utilized to design the guide, taking into account anatomical structures, implant positions, and surgical requirements. The guide is fabricated using 3D printing or milling techniques, ensuring a precise fit. This process allows for customization to meet individual patient needs, improving surgical accuracy and outcomes. The integration of digital workflows streamlines the fabrication process, making it efficient and reliable for dental professionals.
CDT Codes and Billing
CDT codes are standardized dental codes used for billing and documentation, ensuring accurate reimbursement for surgical guide procedures. They are essential for compliance and proper insurance claims processing.
Understanding CDT Codes for Surgical Guides
CDT (Current Dental Terminology) codes are standardized codes developed by the ADA for dental procedures, including surgical guides. These codes ensure uniformity in billing and documentation, facilitating accurate insurance claims. Each code corresponds to specific dental services, making it easier for providers to communicate with insurers. For surgical guides, CDT codes help in distinguishing between custom and generic guides, ensuring proper reimbursement. They also aid in tracking the procedural steps, from planning to placement, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Understanding these codes is crucial for dental practices to maintain precise records and avoid billing errors, ultimately enhancing patient care and practice efficiency.
ADA Guidelines for Coding
The ADA (American Dental Association) provides specific guidelines for coding dental procedures, ensuring accuracy and compliance. These guidelines are crucial for documenting surgical guide-related procedures, emphasizing precise code selection. The ADA updates CDT codes annually to reflect advancements in dental technology and practices. For surgical guides, these codes help differentiate between custom and generic guides, ensuring proper billing. Dental practices must adhere to these guidelines to maintain accurate records and avoid reimbursement issues. The ADA also stresses the importance of detailed documentation, ensuring transparency in patient care and billing processes. By following these guidelines, providers can ensure compliance with regulatory standards and streamline insurance reimbursement, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and patient outcomes.
Insurance Reimbursement Process
The insurance reimbursement process for surgical guide dental codes involves submitting claims with accurate CDT codes to insurers. Dental practices must ensure proper documentation, including pre-surgical plans and guide specifications, to support claims. Insurers verify the codes and medical necessity, impacting reimbursement amounts. Coverage varies by provider, with some requiring pre-approval for custom guides. Practices should familiarize themselves with payer-specific guidelines to optimize reimbursement. Timely filing and appeals for denied claims are crucial for resolving issues. Understanding insurance policies and adhering to coding standards helps streamline the process, ensuring fair compensation for surgical guide procedures. This step ensures financial clarity and reduces administrative challenges for both providers and patients.
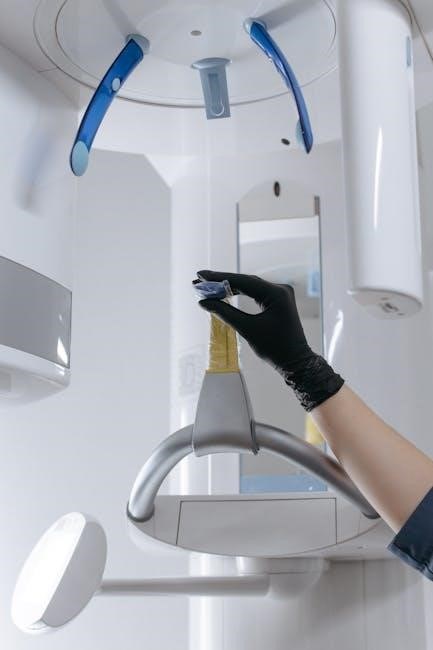
Surgical Guide Placement Procedure
The procedure involves using a custom guide created from CBCT scans and 3D imaging to ensure precise implant placement. Advanced software aids in minimizing errors and complications, while verification ensures accuracy and alignment with treatment plans.
Pre-Surgical Planning and Preparation
Pre-surgical planning involves creating detailed treatment plans using CBCT scans and 3D imaging to assess patient anatomy. Custom surgical guides are designed to match the patient’s jaw structure, ensuring precise implant placement. The process includes evaluating bone density, nerve locations, and surrounding tissue to minimize risks. Digital models are generated using CAD/CAM software, allowing for accurate guide fabrication. Clinicians also review medical histories and diagnostic reports to tailor the procedure. Proper sterilization and preparation of the surgical site are critical, along with ensuring all necessary tools and guides are ready. This thorough preparation ensures efficiency and accuracy during the surgical procedure, enhancing patient safety and outcomes.
Step-by-Step Placement Process
The surgical guide is positioned over the patient’s jaw, aligning with anatomical landmarks to ensure accuracy. Guided drills are used to create pilot holes, followed by progressive enlargement to the final implant diameter. The implant is then inserted through the guide, ensuring precise depth and angle. Verification steps, such as checking the fit and alignment, are conducted to confirm proper placement. Any adjustments are made before finalizing the implant position. The process minimizes soft tissue damage and ensures optimal osseointegration. Post-placement, the guide is removed, and the site is assessed for stability and accuracy; This systematic approach enhances surgical precision and reduces complications, ensuring successful implant outcomes.
Post-Operative Care and Follow-Up
After the surgical guide is used for implant placement, patients are advised to follow a detailed post-operative care plan to ensure proper healing. This includes avoiding chewing on the surgical site, adhering to a soft-food diet, and using prescribed oral rinses to prevent infection. Patients are also instructed to avoid smoking and strenuous activities for a specified period. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor healing progress, remove sutures if necessary, and assess the integration of the implant. Regular check-ups are crucial to identify any potential complications early and ensure the implant’s long-term success. Proper adherence to post-operative guidelines minimizes risks and supports optimal recovery and functionality.
Digital Technology in Surgical Guides
Digital technology enhances surgical guide accuracy through CBCT scans and CAD/CAM software, enabling precise customization and integration with implant systems for improved surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
CBCT Scans and 3D Imaging
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans provide high-resolution 3D imaging of oral and maxillofacial structures, enabling precise anatomical data for surgical guides. This technology captures detailed bone density, nerve pathways, and tissue anatomy, ensuring accurate implant placement. By integrating CBCT data with CAD/CAM software, surgeons can create digitally customized surgical guides that align perfectly with patient anatomy. This reduces surgical time, enhances predictability, and minimizes complications. The use of 3D imaging also allows for preoperative simulation, improving treatment planning and patient outcomes. CBCT scans are a cornerstone of modern dental surgery, offering unparalleled precision and reliability in guide fabrication and implant procedures. This digital approach ensures that surgical guides are both patient-specific and highly effective.
CAD/CAM Software for Customization
CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software plays a pivotal role in creating highly customized surgical guides. By integrating data from CBCT scans, CAD/CAM systems generate precise digital models of a patient’s anatomy, allowing for the design of surgical guides tailored to individual needs. This technology enables surgeons to plan implant placement with millimeter accuracy, ensuring optimal positioning and alignment. CAD/CAM software also facilitates the fabrication of guides using 3D printing or milling, offering a seamless transition from digital design to physical production. The customization capabilities of CAD/CAM enhance surgical efficiency, reduce procedure time, and improve overall outcomes. This advanced approach is integral to modern implantology, providing a high level of precision and reliability in surgical guide development.
Integration with Implant Systems
Integration with implant systems is a critical aspect of surgical guide technology, ensuring seamless compatibility between guides and various implant brands. Modern dental software allows for the creation of guides that align perfectly with specific implant designs, enhancing accuracy and reducing surgical complexity. By importing implant libraries into CAD/CAM systems, surgeons can plan and execute procedures with precision. This integration also enables real-time adjustments during surgery, ensuring optimal implant placement. The use of standardized systems and digital workflows facilitates collaboration between dental labs and surgeons, streamlining the process. Proper integration ensures compliance with ADA coding standards, maintaining accurate documentation for billing and patient records. This synergy between surgical guides and implant systems is essential for achieving predictable and successful outcomes in dental implantology.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Legal compliance in surgical guide use involves adhering to ADA and CDT coding standards, ensuring proper documentation, and meeting regulatory requirements for patient safety and data privacy.
Regulatory Requirements
Compliance with regulatory requirements is critical for the use of surgical guides in dental procedures. These guides must adhere to standards set by the American Dental Association (ADA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The ADA’s CDT codes provide a standardized system for documentation and billing, ensuring transparency and accuracy. Additionally, surgical guides must meet FDA guidelines for medical devices, particularly regarding material safety and sterility. Dental practices are also required to comply with OSHA regulations to ensure patient and staff safety during procedures. Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential to demonstrate adherence to these standards. Failure to comply can result in legal consequences, emphasizing the importance of staying informed about evolving regulatory requirements in dental surgery.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential for the use of surgical guides in dental procedures. Detailed records must be maintained, including patient-specific data, guide specifications, and procedure outcomes. Accurate documentation ensures compliance with regulatory standards and facilitates clear communication between dental teams and insurance providers. The use of ADA and CDT codes is critical for billing and insurance reimbursement, requiring precise coding to reflect the surgical guide’s application. Digital documentation tools, such as integrated dental software, streamline record-keeping and improve accessibility. Maintaining thorough records also protects against legal and financial risks, ensuring accountability and transparency throughout the treatment process. Regular audits and updates to documentation protocols are necessary to stay compliant with evolving standards.
Risk Management and Liability
Risk management and liability considerations are critical when using surgical guides in dental procedures. Proper use of these guides requires adherence to regulatory standards and manufacturer guidelines to minimize potential legal and financial risks. Clinicians must ensure that surgical guides are accurately designed and fabricated to avoid errors that could lead to patient harm or legal disputes. Liability may arise from manufacturing defects, improper usage, or inadequate patient consent. Maintaining thorough documentation and following ADA and CDT coding guidelines can help mitigate risks. Additionally, clinicians should stay updated on best practices and comply with local and federal regulations to reduce exposure to liability. Regular training and quality control measures are essential to ensure the safe and effective use of surgical guides in dental surgery.

Case Studies and Examples
Highlighting real-world applications, surgical guides have enhanced complex implant procedures. For instance, a guide improved accuracy in a challenging case, streamlining the process and reducing surgery time, benefiting both clinicians and patients. This example underscores the practical value of surgical guides in modern dentistry, aligning with ADA coding standards for accurate documentation and billing, ensuring seamless integration into clinical workflows.
Successful Dental Implant Cases
CBCT scans and 3D imaging have enabled precise surgical guide creation, leading to highly successful dental implant placements. For example, a complex case involving multiple implants was executed flawlessly using a custom guide, reducing surgery time by 30%. Another case utilized CAD/CAM software to design a guide that ensured optimal implant positioning, resulting in faster healing and improved patient satisfaction. These examples highlight how surgical guides, combined with advanced technologies, enhance accuracy and efficiency in implant procedures. Proper coding and documentation, adhering to ADA standards, ensure seamless billing and compliance, further underscoring the importance of these tools in modern dentistry.
Challenging Scenarios and Solutions
In complex cases with limited visibility or unusual anatomies, CBCT scans and 3D imaging enable precise surgical guide customization, ensuring accurate implant placement. For instance, patients with insufficient bone density may require bone grafting, which can be integrated into the surgical guide design. Additionally, real-time adjustments using CAD/CAM software help address unexpected intraoperative challenges, such as patient movement or anatomical variations. These advanced tools enhance surgical precision, reduce complications, and improve patient outcomes. By leveraging technology and adhering to ADA guidelines, dental professionals can effectively manage challenging scenarios, ensuring successful implant procedures and streamlined documentation processes.

Future Trends in Surgical Guides
Advancements in AI, 3D printing, and biocompatible materials will revolutionize surgical guides, enhancing precision and customization. Integration with real-time data systems will improve outcomes and efficiency.
Advancements in Material Science
Recent advancements in material science are transforming surgical guides, with a focus on biocompatible and durable materials. 3D printing technologies now utilize advanced polymers and resins that enhance fit and longevity. These materials are designed to be sterilizable and resistant to wear, ensuring precision during procedures. Innovations in nanostructured surfaces improve osseointegration, reducing healing times. Additionally, researchers are exploring bioactive materials that promote tissue regeneration, enhancing surgical outcomes. The integration of these cutting-edge materials with digital workflows enables customizable guides tailored to individual patient anatomy. Such developments not only improve accuracy but also contribute to faster recovery and better patient satisfaction, making surgical guides more effective and reliable in modern dental surgery.
AI and Machine Learning Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing the development and use of surgical guides in dentistry. AI algorithms analyze patient data, such as CBCT scans and 3D models, to predict optimal implant placement with unparalleled precision. Machine learning models improve over time, enabling more accurate and personalized surgical guides. AI-driven tools automate complex processes like anatomical landmark detection, reducing manual errors. Additionally, AI enhances real-time data analysis during procedures, allowing for dynamic adjustments. These technologies also facilitate predictive modeling, helping surgeons anticipate potential challenges and outcomes. By integrating AI, the creation and application of surgical guides become faster, more efficient, and highly customized, leading to better patient care and outcomes.
Global Market Growth and Adoption
The global market for surgical guide dental codes is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for precise dental implant procedures. Advancements in digital technology, such as CBCT scans and CAD/CAM software, have enhanced the adoption of surgical guides worldwide. North America and Europe lead the market due to high healthcare expenditure and advanced infrastructure, while Asia-Pacific is emerging rapidly, fueled by rising dental implant awareness and improving accessibility. The growing preference for customized solutions and the expanding geriatric population further accelerate market expansion. Key players are investing in R&D to develop innovative products, catering to the global demand for efficient and accurate dental surgical guides, ensuring widespread adoption across diverse regions.